Hair Transplant
Advanced Services for Hair Restoration
Millions of people experience hair loss globally, which has an effect on everyone’s quality of life and sense of self. Through surgical procedures that have been scientifically proven, modern hair restoration techniques provide effective solutions for androgenetic alopecia, pattern baldness, and other types of hair thinning.
Using cutting-edge technology and scientifically supported surgical methods, professional hair restoration services offer a wide range of treatment options. With minimally invasive techniques that produce results that look natural, these procedures address male pattern baldness, female pattern hair loss, and specific restoration needs.
Comprehending Hair Restoration Surgery
Relocating healthy hair follicles from donor sites to areas where hair is thinning or missing is known as hair restoration surgery. This microsurgical technique provides long-term remedies for pattern hair loss by restoring permanent hair growth in areas that were previously bald or thinning.
Throughout the patient’s lifetime, the transplanted follicles continue to produce hair while retaining their original properties.
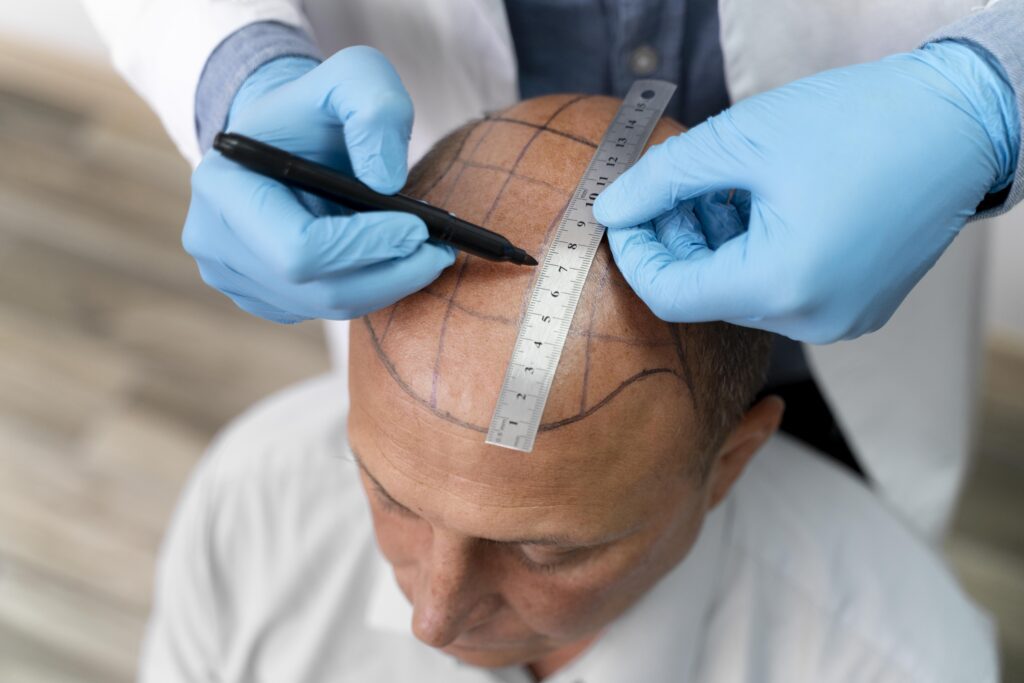

The occipital and parietal parts of the scalp, where hair follicles exhibit genetic resistance to dihydrotestosterone-induced miniaturisation, are commonly considered donor areas. This resistance guarantees that transplanted grafts stay viable and keep growing new, healthy hair.
Surgical Techniques and Methodologies
Technology for Follicular Unit Extraction
The gold standard in contemporary hair transplantation is Follicular Unit Extraction, which harvests individual follicular units using precise equipment. In addition to offering better graft quality and patient comfort, this method does away with the linear scarring that comes with conventional techniques.
Specialised micro-punches with a diameter of 0.7 to 1.0 millimetres are used in FUE procedures to precisely extract intact follicular units. Cutting-edge motorised systems reduce follicle transection rates and tissue damage while increasing extraction efficiency.
Minimal postoperative discomfort, quicker recovery, and the ability to wear short hairstyles without noticeable scarring are just a few benefits of the procedure. When the supply of scalp donors is limited, FUE also makes it possible to harvest body hair.
Methodology of Strip Harvesting
A strip of hair-bearing scalp is removed from the donor area during a follicular unit transplant, and it is then dissected into individual follicular units under a microscope. This method is perfect for extensive restoration requirements because it maximises graft yield in a single session.
Depending on the needs of the patient and the characteristics of the donor area, FUT procedures usually harvest 2000–4000 grafts per session. Careful closure methods reduce scarring while maintaining the integrity of the donor area for possible follow-up operations.
By maintaining follicle viability and minimising handling trauma, stereoscopic dissection guarantees ideal graft preparation and increases transplant success rates. For patients who need extensive coverage in a small number of sessions, this method is still very successful.
Specialized Restoration Applications
Facial hair restoration addresses beard irregularities, mustache deficiencies, and eyebrow reconstruction through targeted follicle placement. These procedures require artistic skill and understanding of natural growth patterns to achieve aesthetically pleasing results.
Eyebrow transplantation utilizes single-hair follicular units placed at precise angles to mimic natural brow architecture. Temporal angle and growth direction consideration ensures results that blend seamlessly with existing brow hair.
Scar revision procedures restore hair growth in areas affected by trauma, previous surgeries, or medical conditions. These specialized applications require careful planning and technique modification to achieve optimal cosmetic outcomes.
Assessing and Choosing Candidates
In addition to having adequate donor hair density and quality, the best candidates for hair restoration show a consistent pattern of hair loss. Reviewing the patient’s medical history, examining their scalp, and determining their goals and expectations are all components of a comprehensive evaluation.
Age considerations require evaluating the trends of hair loss progression and future loss projections in order to develop long-term, sustainable restoration plans. Younger patients may require staged approaches to account for the ongoing progression of hair loss.
Medical contraindications include bleeding disorders, active scalp conditions, and unreasonable expectations regarding outcomes. Psychological evaluation ensures that patients understand the procedure’s schedule and expected results.
Women experiencing female pattern hair loss may benefit from hair restoration when medical treatments prove insufficient. Careful evaluation of hair loss patterns and hormonal factors guides treatment recommendations.
Protocols for Procedures and Recovery
Medication modifications, scalp conditioning, and thorough procedural planning based on specific restoration objectives are all part of pre-operative preparation. Before surgery, patients are given detailed instructions on what to do and what to take.
While enabling active patient participation in graft placement decisions, local anaesthesia guarantees patient comfort throughout the procedure. During extraction and implantation, tumescent anaesthesia techniques improve visibility and reduce bleeding.
Gentle hair washing, activity limitations, and follow-up appointments to track healing progress are all part of recovery protocols. Within 48 to 72 hours, the majority of patients return to their regular activities with little disturbance to their lifestyle.
To maximise graft survival and reduce complications, post-operative care instructions include detailed instructions for hair washing, sleeping positions, and exercise restrictions.
Anticipated Results and Schedule
Usually, 3–4 months after the procedure, the first hair growth starts, and over the next 9–12 months, the density gradually improves. The final results show patterns of natural hair growth that thicken and mature with time.
Transplanted hair responds to styling and treatments normally and needs the same upkeep as natural hair. After healing is finished, patients are free to cut, colour, and style their restored hair as they like.
Modern hair restoration procedures have success rates of over 95% when carried out by skilled surgeons following the right procedures. Graft survival rates are influenced by individual healing traits, post-operative care, and surgical technique.
Medical treatment may be part of long-term care to protect natural hair and stop additional loss in non-transplanted areas. Combination methods maximise patient satisfaction and overall aesthetic results.
Quality Assurance and Standards
Using innovative techniques and artistic talent, board-certified surgeons with specialised training in hair restoration surgery ensure the best outcomes. Through continuous education and technique improvement, current standards of care are upheld.
Guidelines for sterile technique and facility accreditation guarantee patient safety during surgery while lowering the risk of infection. Examples of quality control techniques include graft preparation guidelines and outcome monitoring.
Patients from other nations benefit from comprehensive care coordination, which includes consultation services, treatment planning, and post-operative follow-up protocols. Comprehensive treatment plans and transparent pricing structures help patients make well-informed decisions.
Patient education emphasises realistic expectations, procedural details, and long-term care requirements to ensure satisfaction with restoration outcomes. Comprehensive consultation processes are used to address each person’s goals and concerns.


